
Our latest webinar, Expert Guide to Website Auditing, aims to help you identify and fix some of the top issues we have found when auditing websites.
SEO experts Eden and Taryn joined us to discuss the top 10 site problems and how to fix them. A live Q&A session followed the presentation.
You can watch, listen to or read the discussion by clicking one of the links below.
Watch Expert Guide to Auditing
Listen to Expert Guide to Auditing
Read Expert Guide to Auditing
Top 10 Site Problems (and Solutions)
1. Broken links
Whether internal or external, broken links can negatively impact website rankings and user experience. Search engines see broken links as a sign of poorly maintained and coded websites, while users may lose trust in a site that leads them to non-existent pages. Fixing broken links is easy, and involves finding and investigating them, then either replacing them with relevant pages or removing them. Checking the URL spelling and contacting the server provider can also help fix broken links.
2. Redirects
Redirects send users and search engines to a different URL than initially requested, with three common types being 301, 302, and meta refresh. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that passes ranking power to the new page, while a 302 redirect is temporary. Meta refreshes are executed on the page level and are slower, with a five-second countdown. Redirects can be useful, but improper usages, such as long redirect chains or infinite loops, can damage SEO efforts. These could make it difficult for search engines to crawl the site, slowing load speed and negatively impacting rankings and user experience. To fix these issues, it is best to avoid long chains and loops and redirect each URL in the chain to the final destination page instead of removing redirects for immediate pages.
3. Broken Images
Broken images on a webpage harm SEO rankings and user experience. Identifying the broken image can be done by inspecting or searching the page and then finding out why the image is not displayed, such as a change in location. Changing the image URL in the media gallery is recommended if the image is problematic on multiple pages. If there is no suitable replacement, remove the image from the page while ensuring no blank spaces are left behind.
4. Alt Tags
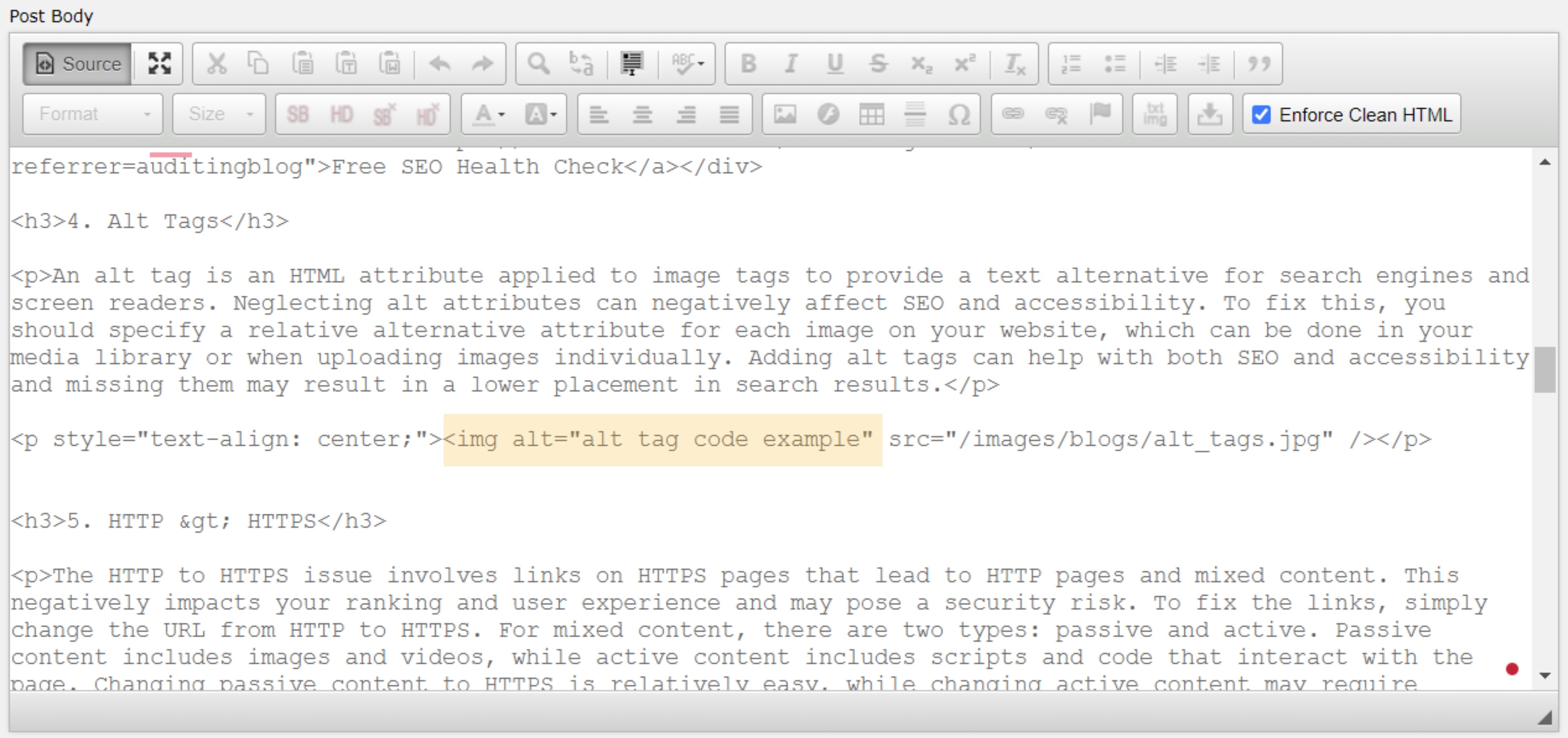
An alt tag is an HTML attribute applied to image tags to provide a text alternative for search engines and screen readers. Neglecting alt attributes can negatively affect SEO and accessibility. To fix this, you should specify a relative alternative attribute for each image on your website, which can be done in your media library or when uploading images individually. Adding alt tags can help with both SEO and accessibility and missing them may result in a lower placement in search results.
5. HTTP > HTTPS
The HTTP to HTTPS issue involves links on HTTPS pages that lead to HTTP pages and mixed content. This negatively impacts your ranking and user experience and may pose a security risk. To fix the links, simply change the URL from HTTP to HTTPS. For mixed content, there are two types: passive and active. Passive content includes images and videos, while active content includes scripts and code that interact with the page. Changing passive content to HTTPS is relatively easy, while changing active content may require significant changes to your website. Nonetheless, ensuring the security of your website is important.
6. Language codes and country codes
It's important to distinguish language and country codes when using hreflang attributes. Country codes like BE are different from language codes like Belarusian, and trying to guess country codes like using UK for the UK is not accurate; UK here is Ukraine. To ensure proper use of hreflang attributes, it's important to specify the correct language and country codes.
7. H1 Tags
Using H1 heading tags is important for providing a clear hierarchy to your content and improving both search engine and user understanding of your page. Multiple H1s can create confusion and negatively impact user experience while having no H1s can lead to a lack of clarity for users. It's best to have a single, clear H1 at the top of your page.

8. Sitemaps
A sitemap file is important for listing all URLs available for crawling, providing easy navigation and better visibility to search engines, and informing them about new or updated content on your website. To fix a sitemap not found issue, generate a sitemap and specify its location in your robots.txt file, and check if Googlebot can index your sitemap through Search Console. Incorrect pages found within the sitemap, such as those with URLs that lead to the same content, redirect to a different webpage, or return a non-200 status code, should be fixed by reviewing the sitemap for any redirected or non-canonical URLs and providing the final destination URLs that are canonical and return a 200 status code.
9. Duplicate and Short Content
The importance of content is discussed in this passage, highlighting that less than 200 words is considered low and not valuable to search engines and users. To avoid keyword stuffing, adding a minimum of 250 words works best. Duplicate content of 85% or more on a page can cause search engines to filter duplicates and lower rankings due to perceived manipulation attempts. Options to fix this include adding unique and relevant content to every page, using canonical links, or adding next and previous link attributes for archives with multiple pages.

10. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink that should be relevant to the page you are linking to rather than generic text. Missing anchor text makes it difficult for crawlers to understand what the page you are linking to is about, and represents a lost opportunity to optimize the performance of the link in search results. The simplest way to optimize anchor text for SEO is to use descriptive text that gives users and search engines an idea of what the target page is about, without over-relying on repetitive keyword-rich phrases, which can be viewed as keyword stuffing and negatively impact SEO.
Q&A
Where do you begin with a site audit?
First, assess the audits and issues on your website and then prioritize them based on the software being used or whether it's being done manually.
Do you need software for a site audit?
We recommend using Google Search Console as it’s free, but there are also paid tools such as SEMRush which give a comprehensive list of issues.
How long does an audit take?
The time it takes to run a site audit depends on the size of your site and how many issues you have on each page. Fixing the issues can be more or less time-consuming depending on the type and number of issues you have. Ultimately, the time you can dedicate to site audits will also impact how quickly you can address any issues that come up.
What is a canonical link?
A canonical tag is used when you have multiple copies of the same page with different languages. You should put a canonical tag on the master page, which is typically the version in the primary language of your website. This will ensure that search engines understand which version of the page is the original and most important and prevent duplicate content issues.
Is there a way to quickly scan for broken links?
You can use Google Search Console, which can notify you of any page indexing issues instead of manually crawling through your site regularly. SEMRush is another option, although it can be pricey.
What is an acceptable site health percentage?
It's recommended to aim for at least a 60 health score, and anything below 50 or 40 should be avoided. The goal is to achieve a 92% health score and get your website to the top 10%.
Are there updates that I should be making regularly to avoid negatively impacting site health?
If you don't regularly add pages to your website, it's recommended to refresh your metadata annually to keep your search results fresh. The frequency of refreshes depends on how often pages are added to the site.
How many of these issues require technical support?
When it comes to fixing website issues, it depends on your level of understanding and access to the website. If you have a WordPress site, it will be easy to fix, but if you have a custom CMS, it may be more difficult. There are free educational tools available, but it's important to research and be careful when fixing technical issues to avoid breaking something major. Practice, time, and reading around the topic can be helpful.
If you’d like to discuss your SEO or content strategy with the team, get in touch here.